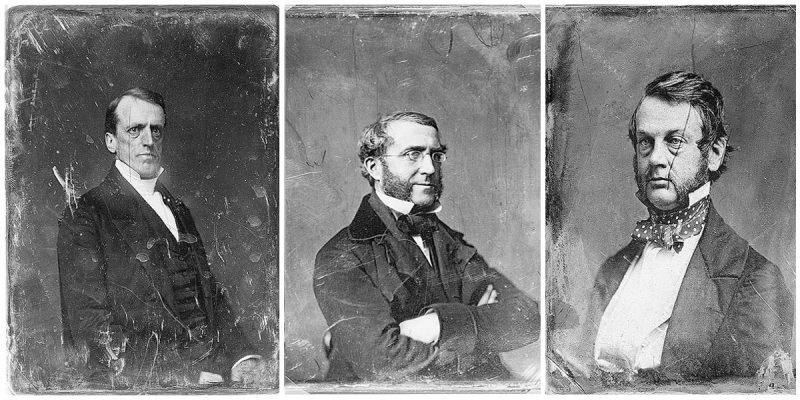The daguerreotype process was the first practicable method of obtaining permanent images with a camera. It was invented by Louis-Jaques-Mandé Daguerre and introduced worldwide in 1839. By 1860, new processes which were less expensive and produced more easily viewed images, had almost completely replaced it. During the past few decades, there has been a small-scale revival of daguerreotypy among photographers interested in making artistic use of early photographic processes.
To make a daguerreotype, the daguerreotypist would polish a sheet of silver-plated copper to a mirror finish; treat it with fumes that made its surface light-sensitive; expose it in a camera for as long as was judged to be necessary, which could be as little as a few seconds for brightly sunlit subjects or much longer with less intense lighting; make the resulting latent image on it visible by fuming it with mercury vapor; remove its sensitivity to light by liquid chemical treatment; rinse and dry it; then seal the easily damaged result behind glass in a protective enclosure.
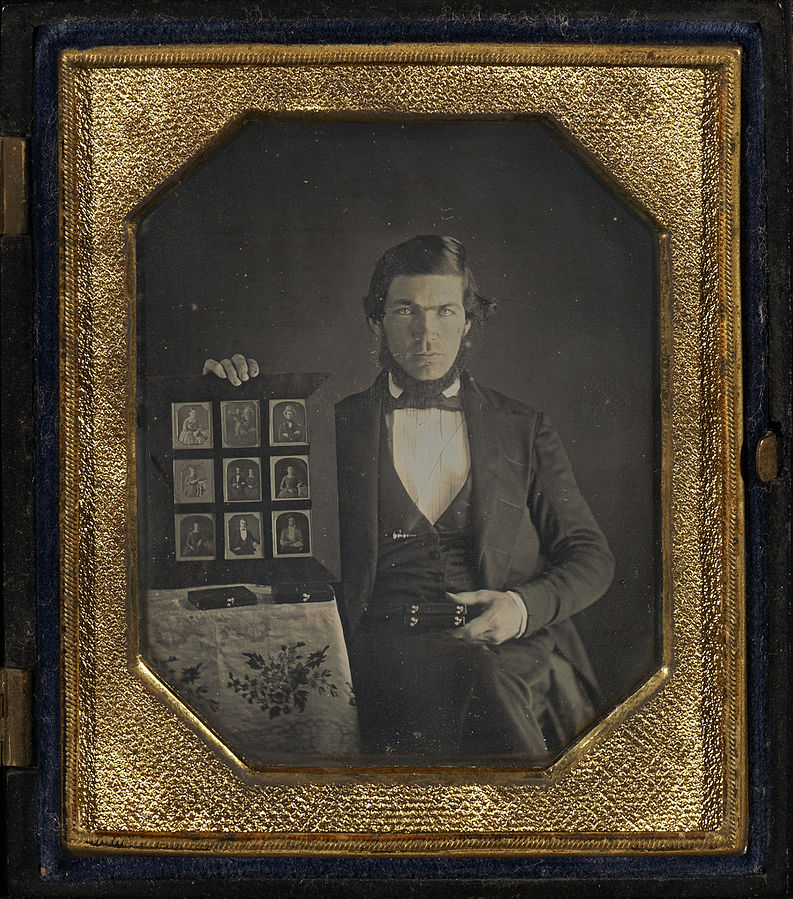
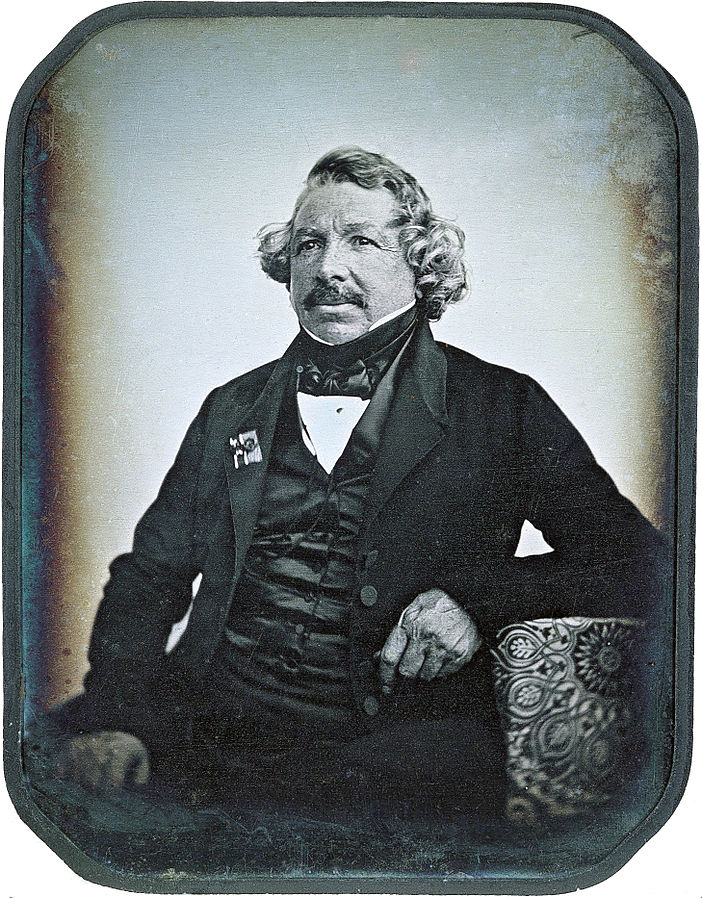
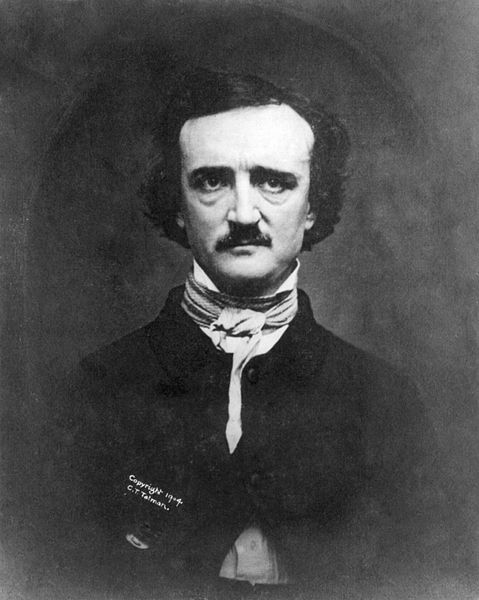
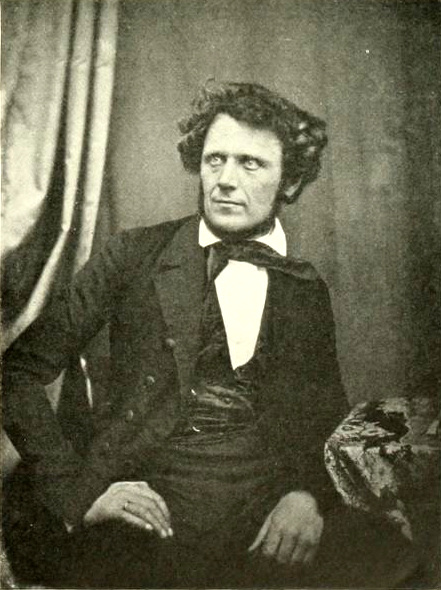
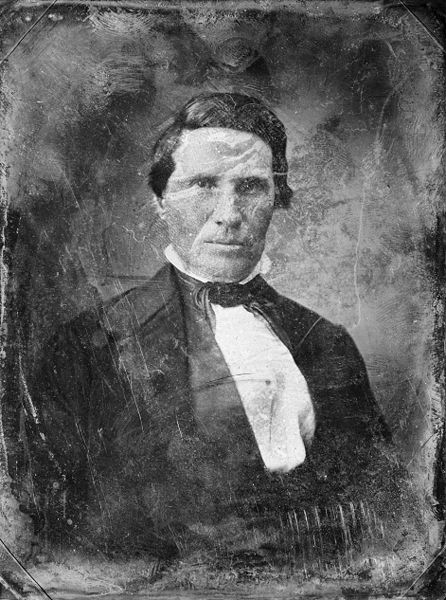
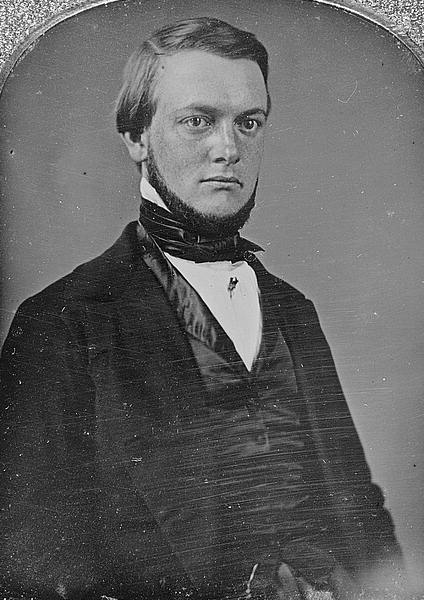
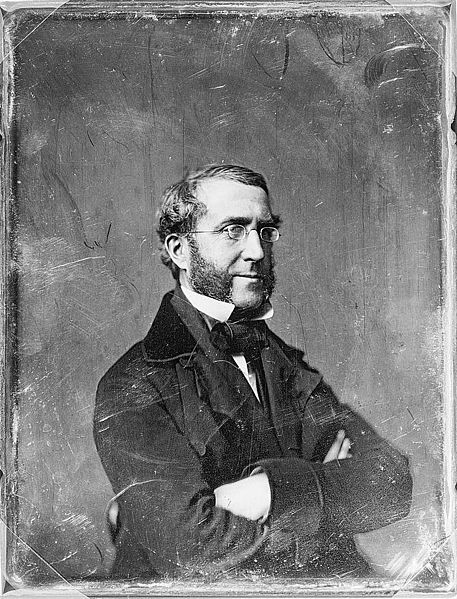
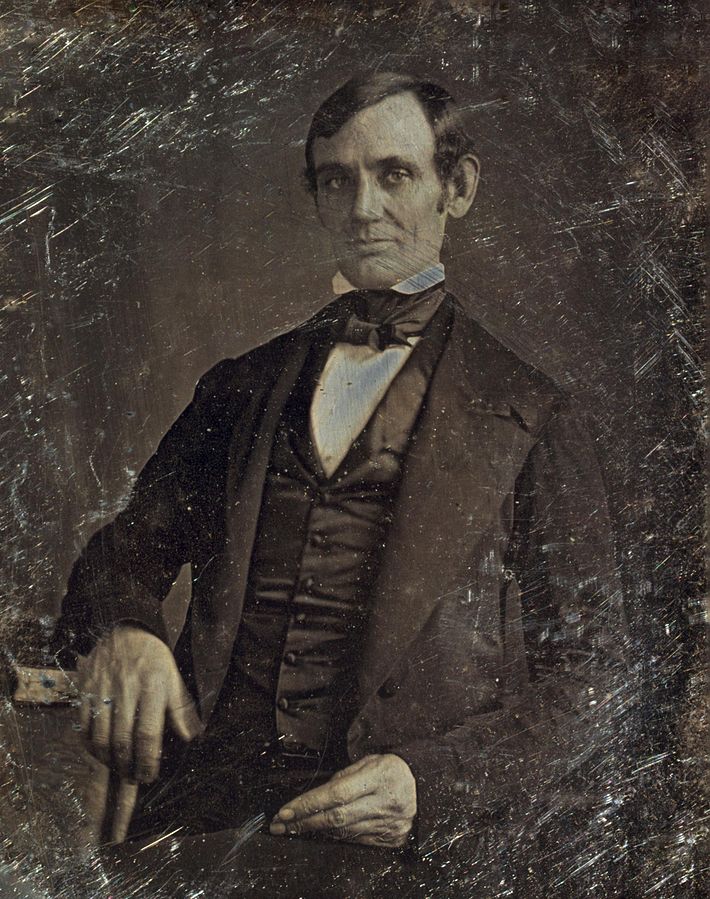
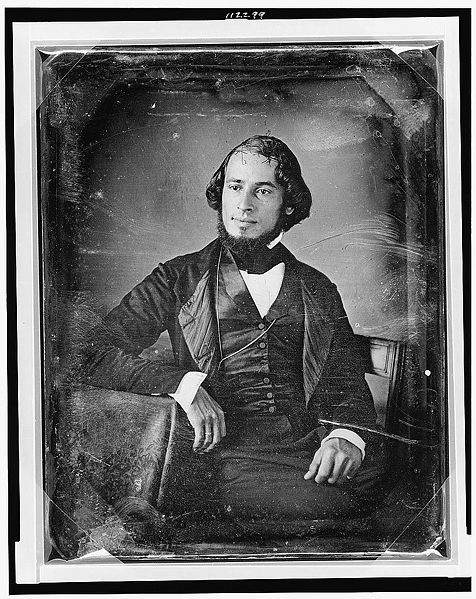






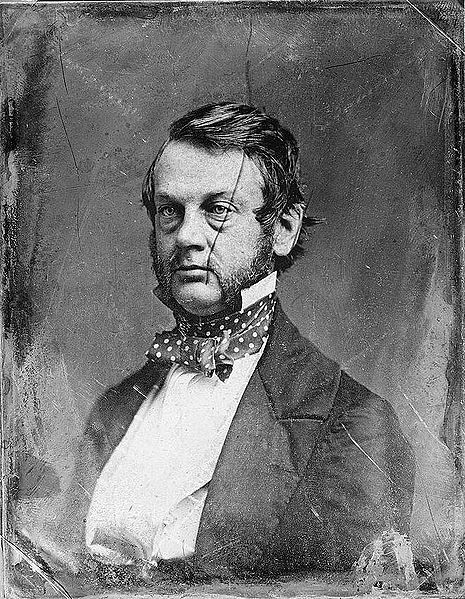




Each daguerreotype is a remarkably detailed, one-of-a-kind photographic image on a highly polished, silver-plated sheet of copper, sensitized with iodine vapors, exposed in a large box camera, developed in mercury fumes, and stabilized (or fixed) with salt water or “hypo” (sodium thiosulphate). The image does not sit on the surface of the metal, but appears to be floating in space, with the illusion of reality, especially with examples that are sharp and well exposed is unique to the process.
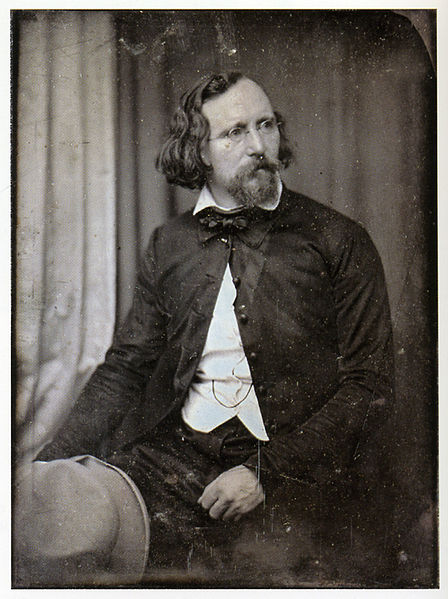
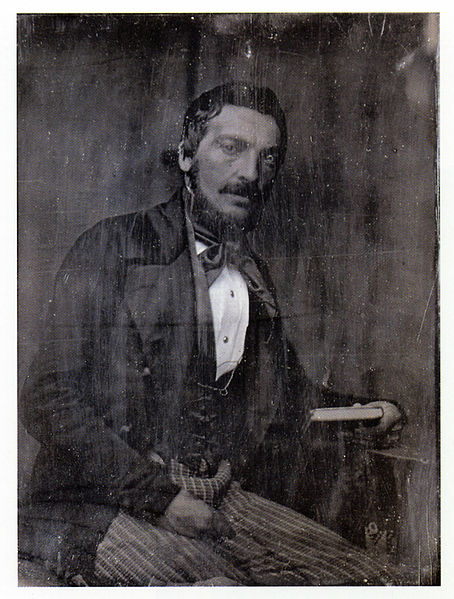
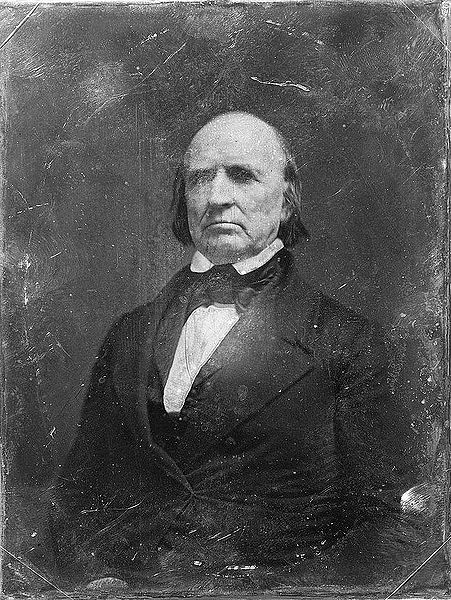
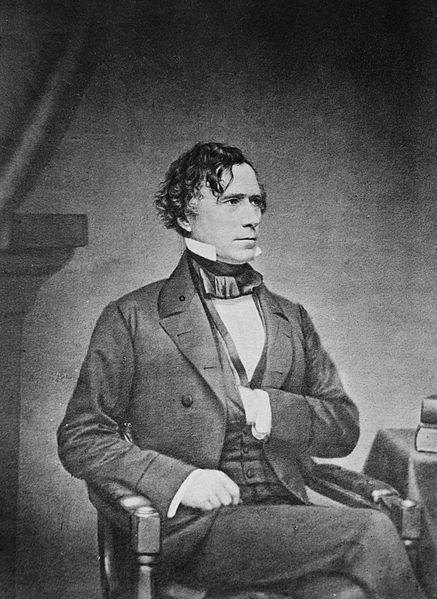
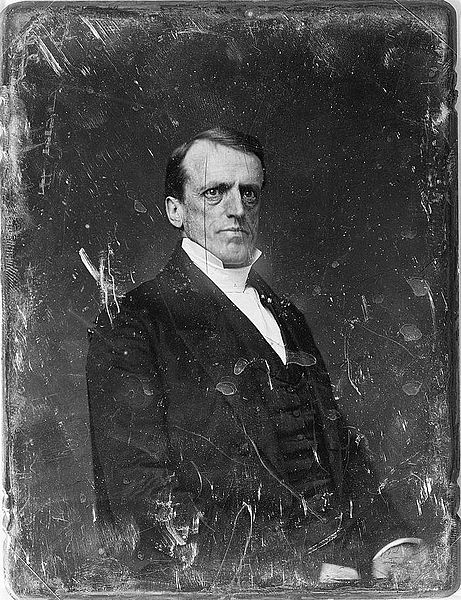
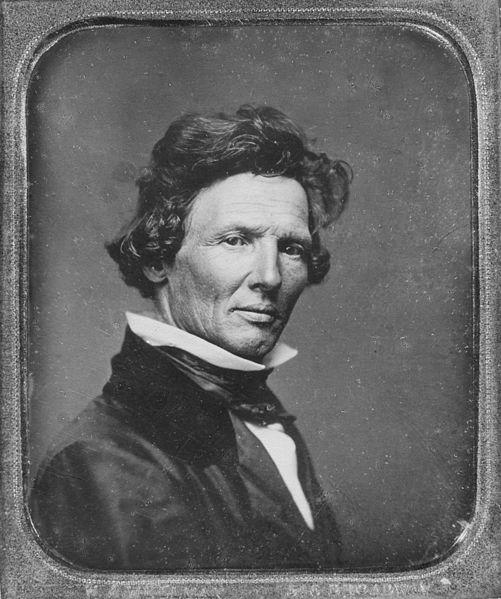
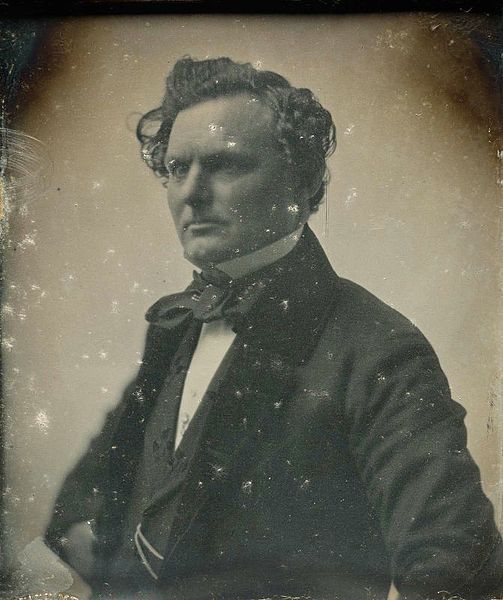
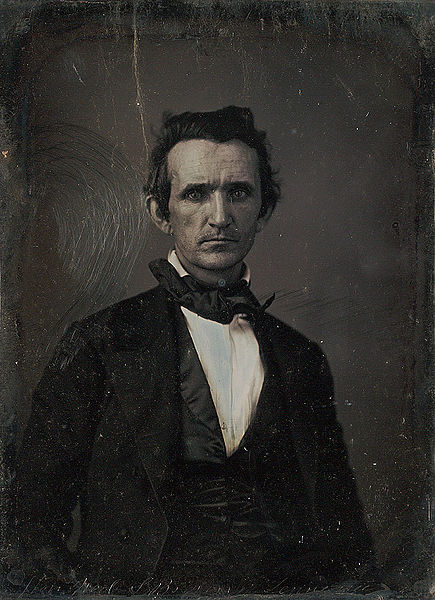
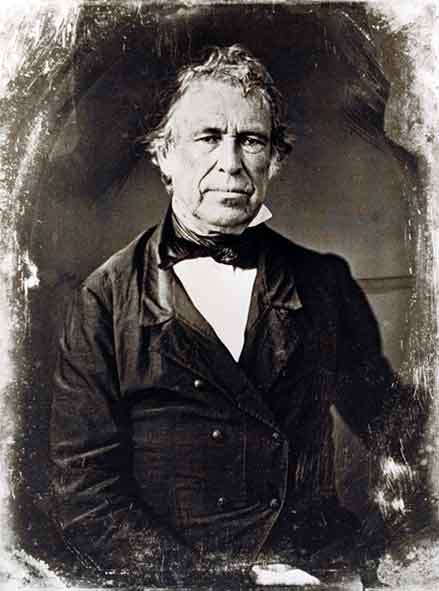
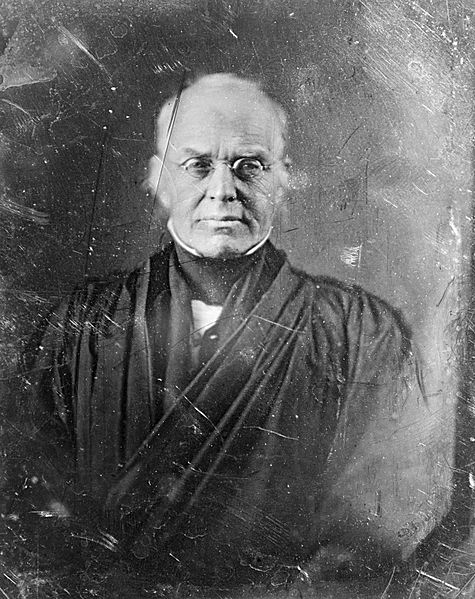










Several types of antique photographs, most often ambrotypes and tintypes, but sometimes even old prints on paper, are very commonly misidentified as daguerreotypes, especially if they are in the small, ornamented cases in which daguerreotypes made in the US and UK were usually housed. The name “daguerreotype” correctly refers only to one very specific image type and medium, the product of a process that was in wide use only from the early 1840’s to the late 1850’s.
Although the daguerreotype process is sometimes said to have died out completely in the early 1860’s, documentary evidence indicates that some very slight use of it persisted more or less continuously throughout the following 150 years of its supposed extinction. The daguerreotype experienced a minor renaissance in the late 20th century and the process is currently practiced by a handful of enthusiastic devotees; there are thought to be fewer than 100 worldwide.