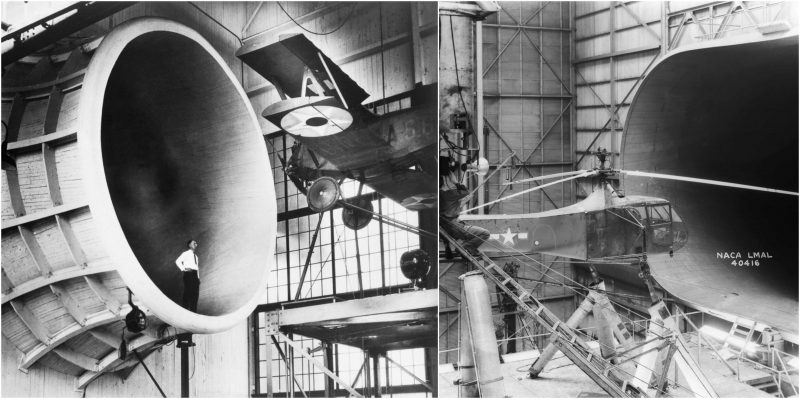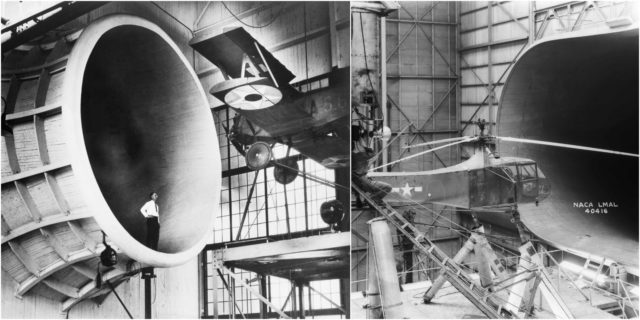
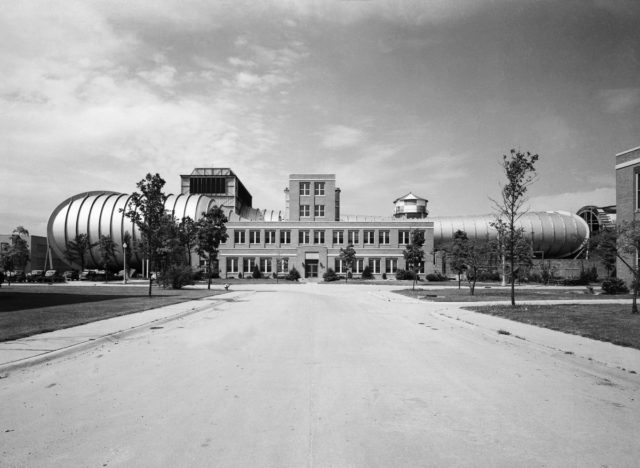
The NASA Ames Research Center wind tunnels are known not only for their immense size, but also for their diverse characteristics that enable various kinds of scientific and engineering research.The Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel (UPWT) was completed in 1956 at a cost of $27 million under the Unitary Plan Act of 1949. Since its completion, the UPWT facility has been the most heavily used NASAwind tunnel. Every major commercial transport and almost every military jet built in the United States over the last 40 years has been tested in this facility. Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft space shuttle models were also tested in this tunnel complex.
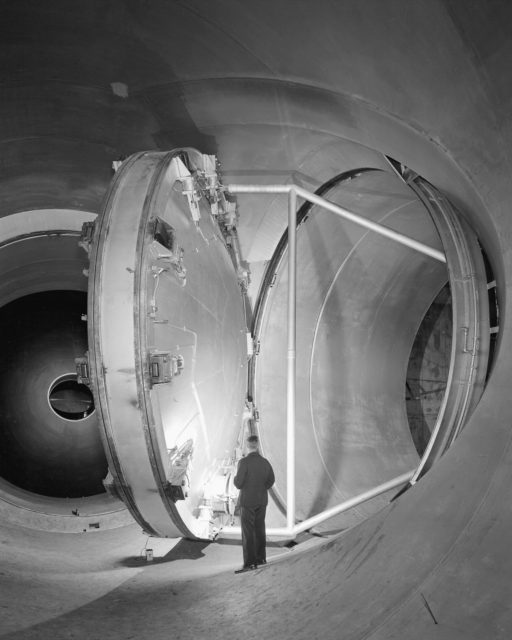
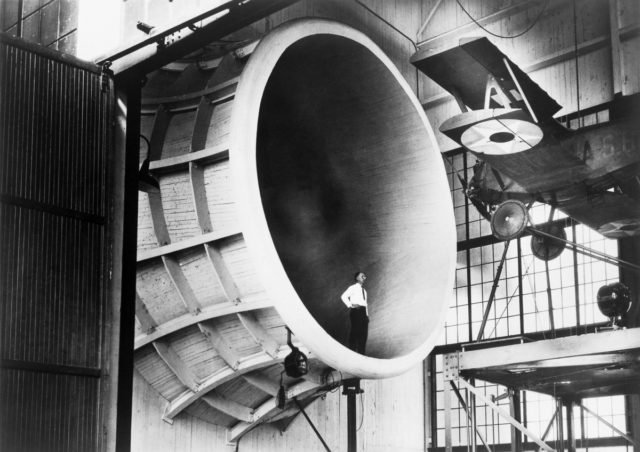
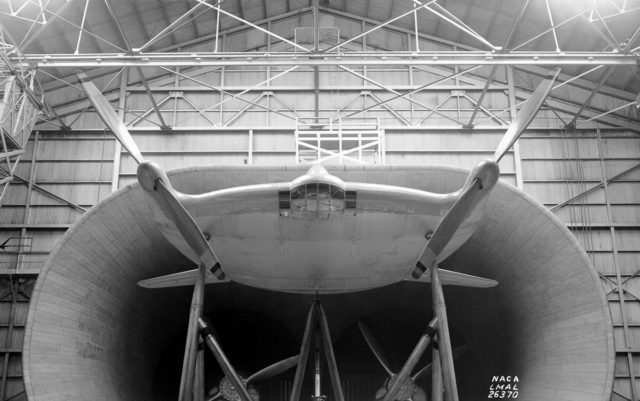
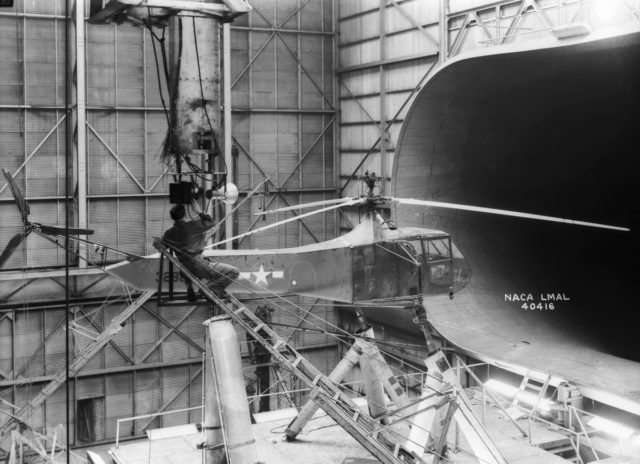
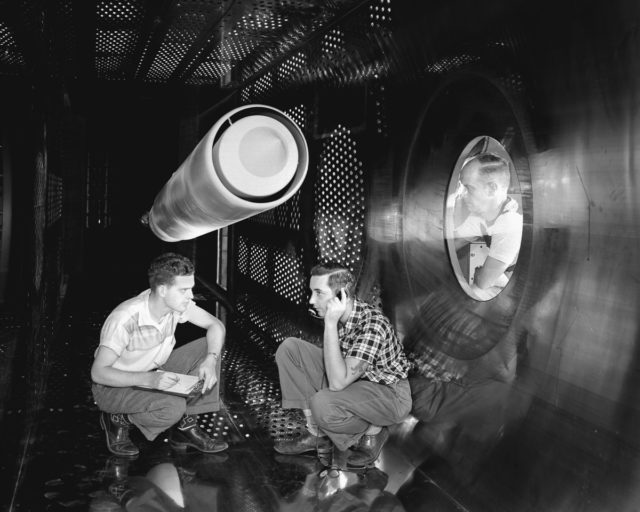
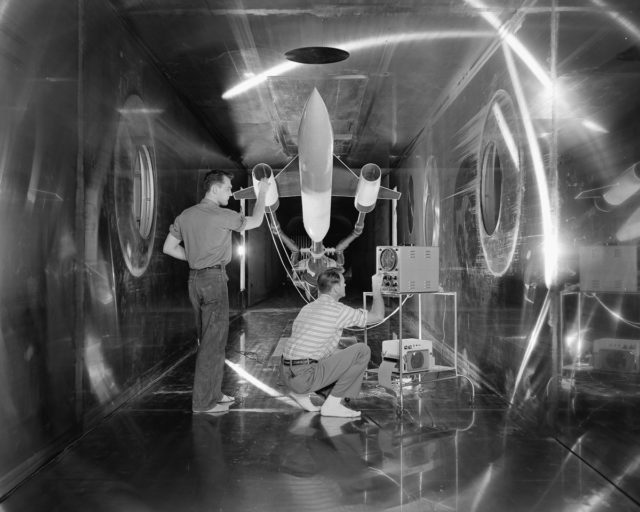







The 40 by 80 foot wind tunnel circuit was originally constructed in the 1940s and is now capable of providing test velocities up to 300 knots (560 km/h; 350 mph). It is used to support an active research program in aerodynamics, dynamics, model noise, and full-scale aircraft and their components. The aerodynamic characteristics of new configurations are investigated with an emphasis on estimating the accuracy of computational methods. Aeromechanical stability boundaries of advanced rotorcraft and rotor-fuselage interactions are explored. Stability and control derivatives are also determined, including the static and dynamic characteristics of new aircraft configurations. The acoustic characteristics of most of the full-scale vehicles are also determined, as well as acoustic research aimed at discovering and reducing aerodynamic sources of noise. In addition to the normal data gathering methods (e.g., balance system, pressure measuring transducers, and temperature sensing thermocouples), state-of-the-art, non-intrusive instrumentation (e.g., laser velocimeters and shadowgraphs) are available to help determine flow direction and velocity in and around the lifting surfaces of models or aircraft undergoing investigation. The 40 by 80 Foot Wind Tunnel is primarily used for determining the low- and medium-speed aerodynamic characteristics of high-performance aircraft, rotorcraft, and fixed wing, powered-lift V/STOL aircraft.
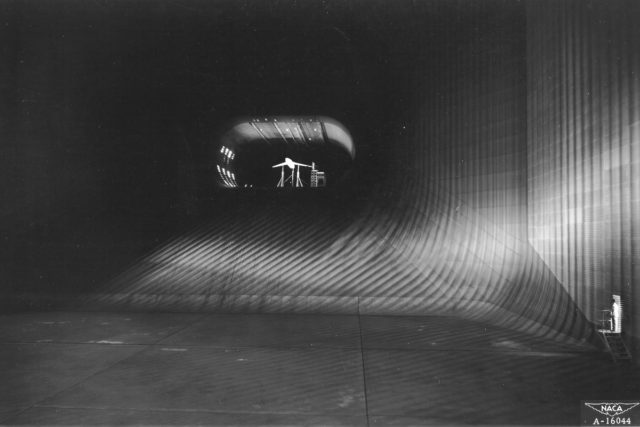
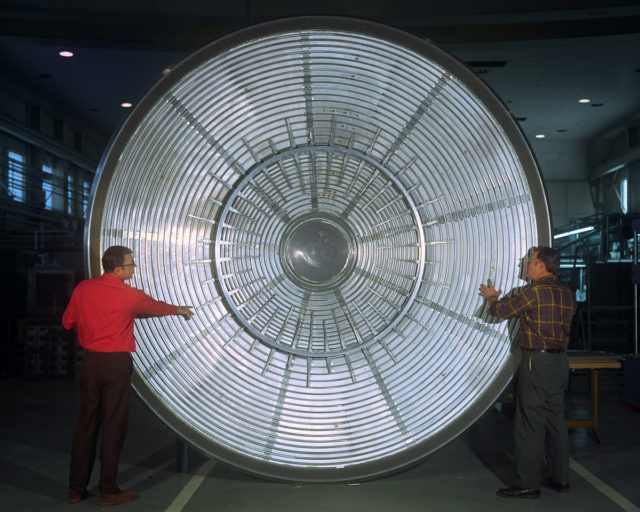
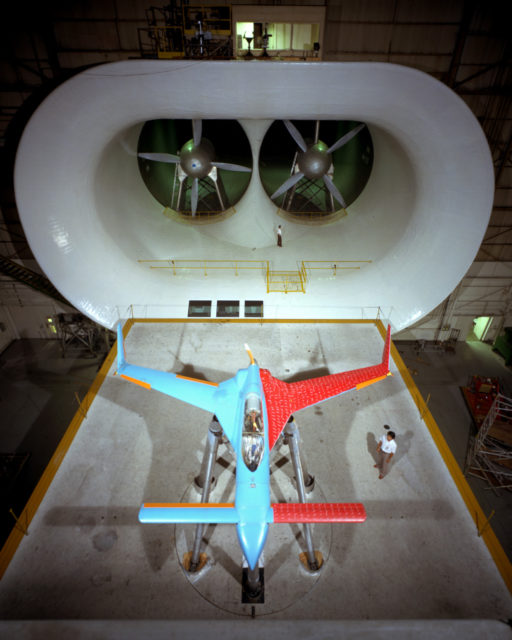
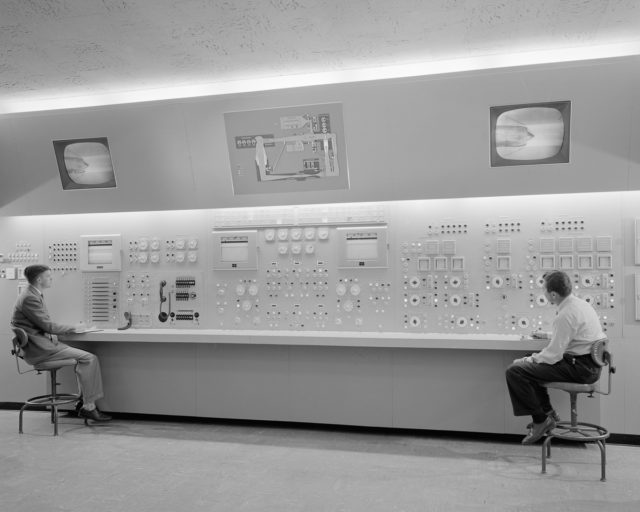




Although decommissioned by NASA in 2003, the NFAC is now being operated by the United States Air Force as a satellite facility of the Arnold Engineering Development Complex
All Photos by NASA