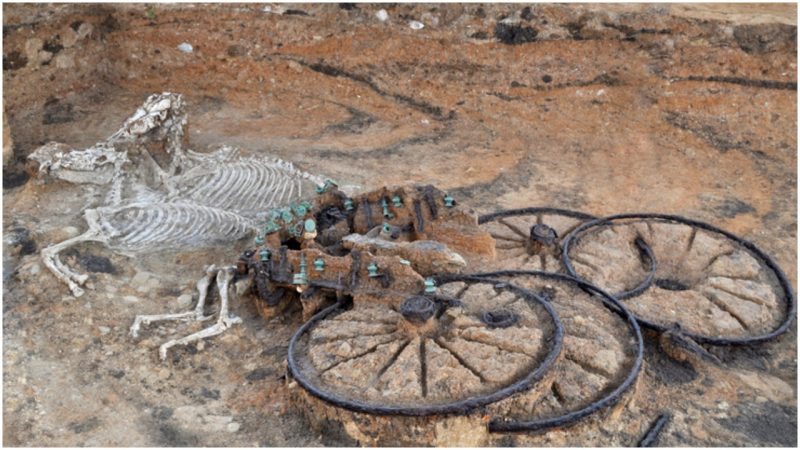
In the second time in two years, an Iron Age chariot has been found buried in a Yorkshire community. The discovery was made in the town of Pocklington, England, at a construction site where more than 200 homes are being built.
As of early October 2018, archaeologists are working to fully excavate the find. Media reports say that not only a chariot but also horse and human remains were discovered.
Simon Usher, managing director at Persimmon Homes Yorkshire, said: “We can confirm that a significant archaeological discovery, featuring an Iron Age horse-drawn chariot, has been made at our development, The Mile in Pocklington. Careful excavation is ongoing by our archaeologists and a thorough investigation is in the process to date and detail the find.”

In a bizarre twist, 18 months ago, another Iron Age chariot was found, along with two horses, at a different construction site in Pocklington. Archaeology Arts reported in 2017: “The chariot was buried as part of a funerary practice that was not uncommon in the Iron Age. However, the horses were a rather surprising addition for archaeologists.”
The Telegraph said that “the find of the remains dating back to 500 BC is the first of its kind in the last 200 years and one of only 26 chariots ever excavated in the UK.”

Archaeologists say it is highly unusual for a horse and chariot to be buried together and with a human. In 2017, Paula Ware, managing director at MAP Archaeological Practice Ltd, told a reporter, “The chariot was located in the final square barrow to be excavated and on the periphery of the cemetery.”
She continued, “The discoveries are set to widen our understanding of the Arras (Middle Iron Age) culture and the dating of artifacts to secure contexts is exceptional.”

A chariot was the possession of a high-status individual. The rite of including horses as part of the burial is being puzzled over by researchers. Before finding the chariot, the dig at the Burnby Lane site revealed artifacts including a sword, shield, spears, brooches, and pots. The excavations give insight into life over 2,500 years ago. These are thought to be people of the Arras culture.
Yorkshire continues to be the place where astoundingly well-preserved remains of the Arras culture are found. In 2016, some 150 skeletons and their personal possessions were discovered in a small market town at the foot of the Yorkshire Wolds.
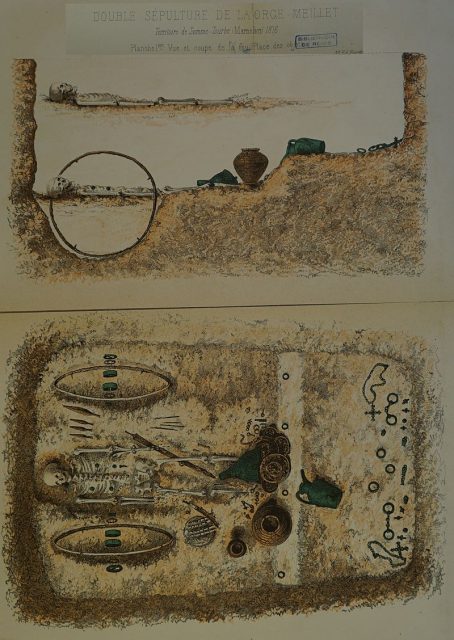
Some of the 75 square barrows, or burial chambers, contained personal possessions such as jewelry and weapons, according to The Guardian. Archaeologists also discovered a skeleton with a shield.
Media reports say those remains were of a man in his late teens or twenties, who died with his sword at his side. Before his death he reportedly had six spears pressed into him “like a hedgehog.”
It is believed these sites all date to the Iron Age, which in Britain lasted from 800 BC until the time of the Roman conquest, beginning in 43 AD.
An in-depth study will focus on whether the population is indigenous or were recent arrivals from the Continent. Archaeologists also hope to reveal how those buried at the site died and whether or not they are related in anyway, as well as potential DNA analysis.
Read another story from us: Identity Finally Revealed of the Mysterious ‘Woman in the Iron Coffin’
The custom of burying the deceased with their chariots within squares is unknown in the rest of the British Iron Age. Interestingly, the Arras vehicles were usually disassembled, a practice less common in the Continental chariot burials.
